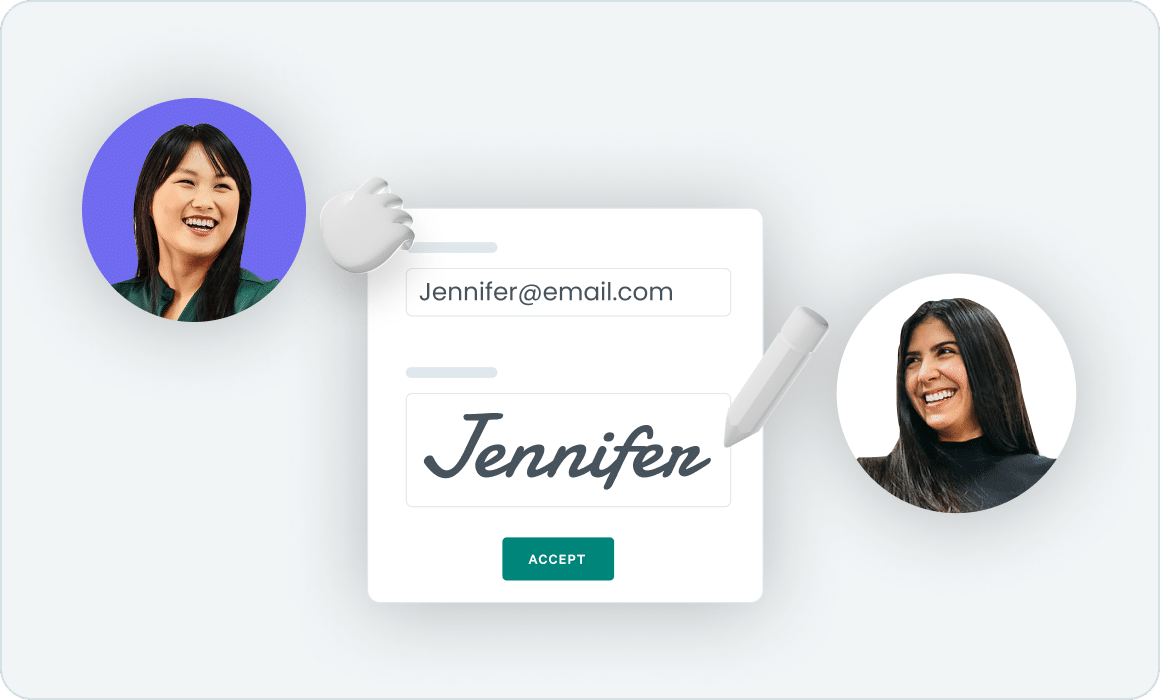
Chasing down signatures is a headache. Whether it's waiting for a client to print, sign, scan, and email a document back—or worse, mailing paperwork back and forth—traditional signing methods slow everything down. Deals stall, projects get delayed, and your team wastes time on unnecessary back-and-forth.
That’s why electronic signatures or e-signatures were created. They offer plenty of benefits. You can save time and money. But, perhaps less obviously, you create stronger relationships with clients and make work easier on your staff.
But, now you’re probably wondering what the three different types of electronic signatures are.
Let’s find out.
Key Takeaways
- An electronic signature (e-signature) is a signature collected electronically to signify agreement on a contract or other document.
- The three types of e-signature are a Simple Electronic Signature, an Advanced Electronic Signature, and a Qualified Electronic Signature.
- Qwilr offers an e-signature feature within our contract and proposal templates to streamline the closing process.
What is an electronic signature?
An electronic signature is just what it sounds like — a signature that is captured electronically. According to the E-Sign Act at the FDIC, an electronic signature can be “an electronic sound, symbol, or process, attached to or logically associated with a contract or other record and executed or adopted by a person with the intent to sign the record.”
In short, any mark made by the person who wants to sign an official document can be captured as an e-signature. It could be a signature created with a mousepad or a picture of a handwritten signature, for example.
More and more organizations are using e-signatures to help people file official documents, so they’ve gotten increasingly creative in finding ways to capture those signatures.
How is an e-signature verified?
In general, the person collecting the e-signature must verify the identity of the signer at the time of the signature. This verification can be performed in person or over a video conference call.
The type of e-signature will determine how stringent the protocols for identification must be.
The 3 types of electronic signatures
The primary difference between the three main types of electronic signatures relates to simplicity versus complexity. The three types of e-signatures are:
Simple Electronic Signatures (SES)
The broadest e-signature used is the SES or Simple Electronic Signature. It can be accepted by whoever happens to be collecting the signature without first verifying the identity of the signer.
It may be used in medical consent forms, HR documents, sales contracts, or other low-risk agreements.
For more high-level security, you’ll want a bit more complexity.
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES)
The Advanced Electronic Signature does require authentication of the identity of the signer, and the collector of the signature must carry a Certificate of Authority to certify the signature.
This certificate will uniquely identify the singer of the electronic documents.
AES are often used in high-risk transactions like financial transfers of large amounts of money, tax returns, legal documents like partnership agreements, and work contracts like new hire paperwork.
Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES)
The highest level of security in e–signatures would be the QES, or Qualified Electronic Signature. A QES is often referred to as a digital signature. Though the two terms, electronic signature and digital signature, are often used interchangeably, the two are not the same.
A digital signature is a type of electronic signature that requires a certificate based on public key issues with technological means. In this case, the person or organization collecting the signature must be authorized by a public office to become a qualified trust provider (QTSP), an audited entity.
The QTSP can then verify the identity of the signer in person or over video chat, as long as the identification is face-to-face.
QES are typically used on sales contracts, large financial transactions, and legal documents.
Examples of e-signatures
You may have heard of the many companies that now provide e-signature options for businesses. DocuSign and Adobe are perhaps two of the biggest names in the e-signature game. But today, a growing number of businesses that help you create content and organize documents are all offering an e-signature feature that allows you to get all of your proposal and contract creation taken care of in one location.
Qwilr is an excellent example of a company that provides multiple services, and the e-signature is just one of them.
Qwilr’s e-signature feature offers the highest level of security and a complete audit trail that applies globally.
The e-signatures collected on Qwilr documents are compliant with the E-SIGN ACT and the UETA in the USA as well as in many countries around the world.
Examples of e-signatures include a scanned handwritten wet signature, a typed name, and even an X. The primary requirement to meet e-signature standards at the highest level of compliance is that the signer has both intent and understanding.
For this reason, the Qwilr audit trail includes contact details of the signer, the IP address and timestamp of the first visit to the page, links to stored backups of any projects worked on, and a record of emails sent to all parties.
Essentially, we show a paper trail that links the signature back to the signer, showing clear intent and understanding.
Who uses e-signatures?
Anyone drafting a formal agreement can collect e-signatures, but the most common uses include:
- Sales contacts
- Employment contracts
- Purchase orders
- Real estate contracts
- Vendor contracts
- IP licensing agreements
- Legal agreements
- Non-disclosure agreements
In each of these cases, the person collecting, or requiring, the signature will need to determine how much security they want involved in the e-signature process. But from a legal point of view, it’s always a good idea to have more security than less.
Is an electronic signature legally binding?
At the end of the day, if you do end up in court, you want to have the tightest audit trail possible. That’s why Qwilr offers these audit trails for every e-signature our clients add to their contracts and proposal templates.
After all, the only reason to collect a signature from anyone is to have a signed agreement of some sort. The only reason for getting a signed agreement is to hold the signing parties accountable.
E-signatures are legally binding and safe for your business, but when it comes to accountability, you’ll need to show intent and understanding.
Without a proper audit trail, it can be hard to do that sometimes.
Thus, it always makes sense to have that audit trail.
Learn more about what Qwilr can do for your business today
In the end, an e-signature can save you time and money because you don’t have to create a physical paper trail and physically chase someone down to get their signature.
But you want to make sure you’re getting the right e-signature and that you make it as easy as possible to capture for the signer as possible.
That’s how you close deals.
If you want to learn more about closing deals, creating contracts or proposals, or adding the e-signature feature to your documents, book a demo with Qwilr.
We’ll show you how we can help streamline your business and sales processes while making them more interactive and engaging for your potential clients.
About the author

Brendan Connaughton|Head of Growth Marketing
Brendan heads up growth marketing and demand generation at Qwilr, overseeing performance marketing, SEO, and lifecycle initiatives. Brendan has been instrumental in developing go-to-market functions for a number of high-growth startups and challenger brands.