"The times, they are a-changin'" — Bob Dylan
We often refer to ‘putting pen to paper’. But unless you are J.K. Rowling who began noting her first ideas of Harry Potter on a napkin while seated on a train, you’re most likely using a device to make your notes.
Yes, the world has become digitalized. So yes, the need for secure, efficient, and legally binding methods of signing documents has never been greater.
Two buzzwords we’re going to hear a lot: ‘digital signatures’ and ‘e-signatures.’ What are they and how do you choose the right solution for your needs?
Key Takeaways
- E-signatures are versatile and convenient: E-signatures include methods like typing your name or clicking a button, making them perfect for everyday transactions.
- Digital signatures offer advanced security: Digital signatures use cryptographic technology to ensure document authenticity and protect against tampering, making them ideal for high-security transactions.
- Different needs require different solutions: E-signatures work well for routine, low-risk agreements, while digital signatures are essential for sensitive documents.
- Both solutions are legally binding: E-signatures are legally accepted for most documents, while digital signatures provide extra security and compliance.
- Qwilr helps businesses streamline the signing process without sacrificing security or legality.
What are e-signatures?
E-signatures, short for electronic signatures, are a broad category of methods used to sign documents electronically. According to the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (E-SIGN Act) in the United States and similar regulations worldwide, an e-signature is any electronic sound, symbol, or process attached to or logically associated with a record and executed with the intent to sign that record.
In practice, e-signatures come in all shapes and sizes, like digital fingerprints leaving their mark in the virtual world:
- Typing your name at the end of an email.
- Clicking an “I Agree” button.
- Using a stylus or finger to sign on a touchscreen device.
- Uploading a scanned image of your handwritten signature.
E-signatures are designed to provide convenience and simplicity. They are widely accepted in most business transactions, including contracts, agreements, and forms, provided they meet the legal requirements of intent, consent, and association with the signed document. Essentially, they put the “e” in easy signing. (Okay, that may sound salesly but you get the gist)

Types of e-signatures
E-signatures come in various forms, each catering to different needs and levels of security:
- Click-to-sign: Simple actions like checking a box or clicking a button to indicate agreement. These are common for terms and conditions.
- Drawn signatures: Using a stylus, finger, or mouse to replicate a handwritten signature on a digital device.
- Image-based signatures: Uploading an image of a handwritten signature and placing it on a document.
- Certificate-based signatures: Tied to specific digital certificates for enhanced authenticity and traceability.
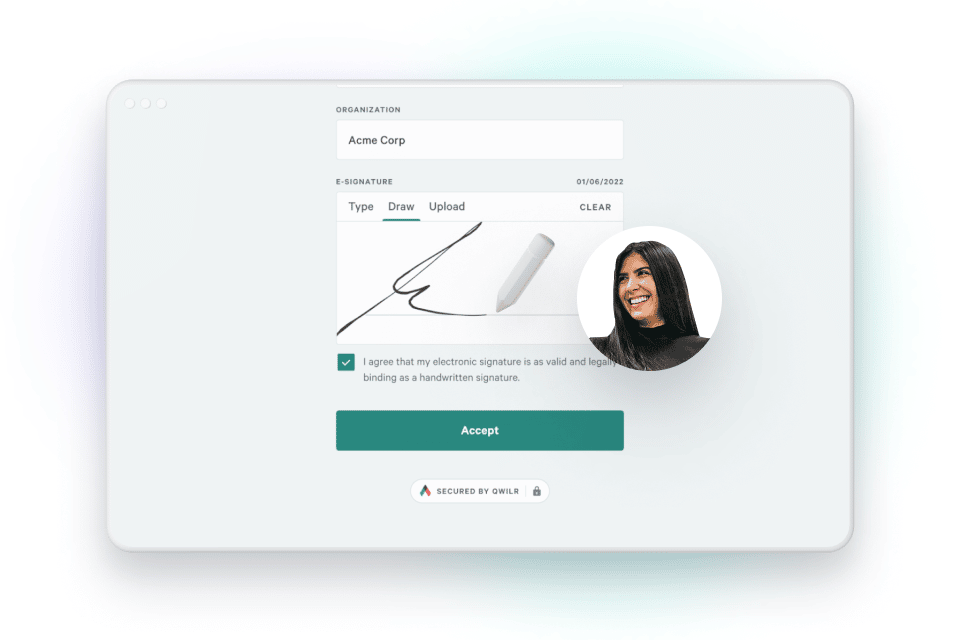
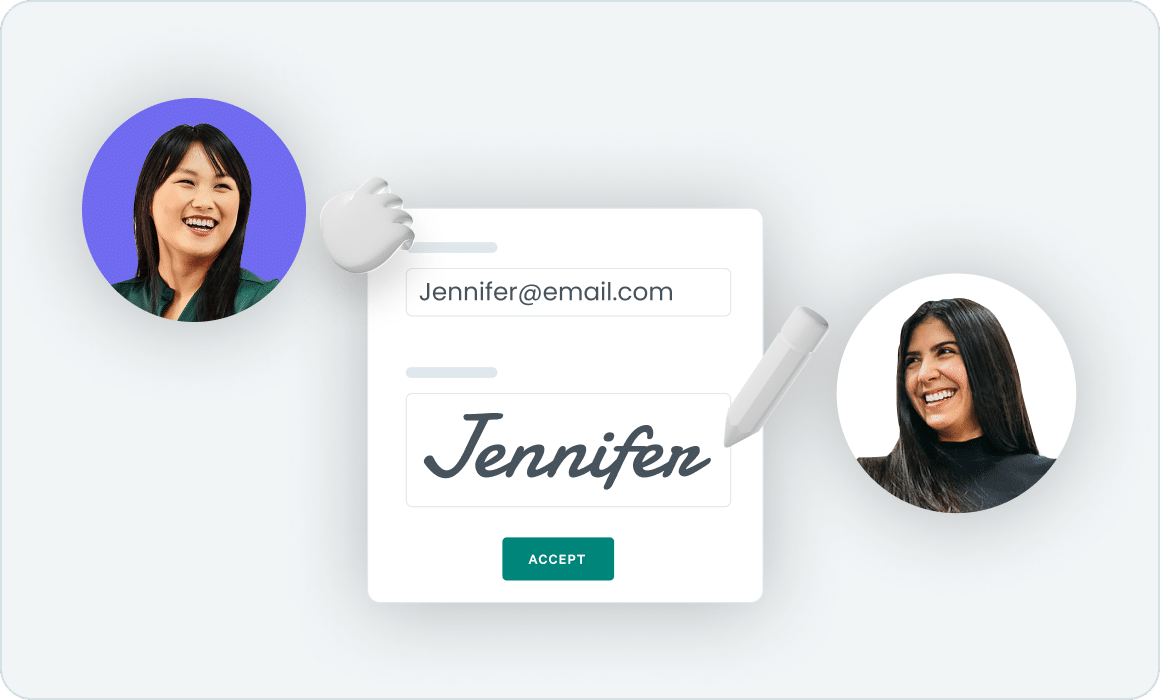
Signees can upload, draw, or type legally binding signatures in Qwilr documents
What are digital signatures?
Digital signatures, a subset of e-signatures, are a more advanced and secure method of signing documents electronically. They rely on cryptographic algorithms to ensure the authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation of a document. (Sounds intense, yes!). Digital signatures use a process called Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to verify the identity of the signer and to protect the signed document from tampering.
Stay with us here. This is how digital signatures typically work:
- The signer is issued a unique digital certificate by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
- When signing a document, the signer’s private key (a component of the digital certificate) creates a unique encrypted hash of the document.
- The recipient uses the signer’s public key to decrypt the hash and verify the document’s authenticity and integrity.
Digital signatures are widely used in industries where security and compliance are critical, such as finance, healthcare, and government, acting as the lock and key to ensure sensitive information stays secure.
Types of digital signatures
Digital signatures come in all secured shapes and sizes - classified by how locked down and signed up they are:
- Basic electronic signatures: Provide minimal security and are often used for low-risk transactions.
- Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES): Require unique identification of the signer and provide greater assurance of authenticity.
- Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES): Top-notch security, these are created using a secure device and a digital certificate issued by a trusted CA. They comply with the strictest regulations, such as the EU’s eIDAS.
Key differences between digital signatures and e-signatures
While both digital signatures and e-signatures enable the electronic signing of documents, there are some pretty significant differences between the two in terms of security, technology, and application. Let’s break them down:
1. Technology
- E-signatures: E-signatures rely on simpler technologies, such as graphical representations of signatures, and are often implemented through software platforms that track the signer’s actions.
- Digital signatures: Digital signatures use cryptographic technology and PKI, making them far more secure and tamper-proof.
2. Security
- E-signatures: Security measures for e-signatures depend on the platform used. While they may include audit trails or password protection, they are generally less robust than digital signatures.
- Digital signatures: Digital signatures offer a higher level of security by encrypting the document and verifying the signer’s identity through a trusted CA.
3. Legality
- E-signatures: E-signatures are legally binding in most jurisdictions under laws like the E-SIGN Act and the European Union’s eIDAS Regulation, provided they meet specific criteria.
- Digital signatures: Digital signatures are also legally binding but offer stronger compliance with stringent regulations like those in the healthcare and financial sectors.
4. Use cases
- E-signatures: Best suited for everyday transactions where convenience is a priority, such as signing contracts, NDAs, and HR documents.
- Digital signatures: Ideal for high-security scenarios, such as financial transactions, medical records, and government communications.

5. Verification process
- E-signatures: Verification often depends on the signer’s intent and may include additional measures like email verification or audit trails.
- Digital signatures: The verification process is built into the cryptographic system, ensuring a more reliable method of proving authenticity and integrity.
Think of e-signatures as a selfie - a quick, convenient way to sign something electronically.
Digital signatures, on the other hand, are like a passport - verified, encrypted, and stamped with extra security to prove you’re the real deal.
One is fast and easy, the other is official and airtight!
Real-world examples
Coming up: the practical applications of e-signatures and digital signatures. Let’s consider two hypothetical situations:
Scenario 1: Using an E-Signature
Martha is a freelance graphic designer working with a new client, John. John sends her a contract outlining the terms of their agreement, including payment details and project deadlines. To quickly finalize the agreement, Martha uses an e-signature platform like Qwilr to sign the document. Since the contract is a standard business agreement and doesn’t involve sensitive or high-risk information, an e-signature is sufficient and legally binding. Done deal, easy peasy.
Scenario 2: Using a digital signature
Dr. Patel is a researcher submitting a grant proposal to a government agency. The proposal contains sensitive data and must comply with strict regulatory requirements. To ensure the document’s authenticity and integrity, Dr. Patel uses a digital signature issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). The digital signature not only verifies Dr. Patel’s identity but also ensures that the document hasn’t been altered after signing, meeting the agency’s high-security standards.
Advantages of e-signatures
E-signatures offer several benefits that make them a popular choice for businesses and individuals:
- Convenience: E-signatures allow users to sign documents anytime, anywhere, using a variety of devices.
- Cost-effectiveness: By eliminating the need for printing, scanning, and mailing, e-signatures save time and money.
- Eco-friendly: Going paperless reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional document signing - big yay.
- Ease of integration: Many e-signature tools like Qwilr and Docusign integrate seamlessly with popular productivity tools and CMS.
Advantages of digital signatures
Digital signatures offer unique advantages that make them indispensable in high-stakes scenarios:
- Enhanced security: Digital signatures ensure that the document’s content cannot be altered without detection.
- Identity verification: By using trusted CAs, digital signatures provide robust authentication of the signer’s identity.
- Compliance: Digital signatures meet the requirements of strict regulatory standards, including HIPAA, GDPR, and SOX.
- Global acceptance: World standards - digital signatures are recognized and accepted worldwide, making them ideal for international transactions.
Choosing the right solution
When deciding between e-signatures and digital signatures, consider the following factors:
1. Nature of the transaction
For routine transactions where security is less critical, such as signing a formal or non-disclosure agreement or a lease, e-signatures do the trick.
For sensitive transactions requiring high levels of security, such as financial contracts or healthcare records, digital signatures are the better choice.
2. Legal and regulatory requirements
If your industry is subject to strict regulations, such as the financial or healthcare sectors, digital signatures are likely a necessity.
For general business use, e-signatures typically meet legal requirements.
3. Budget and resources
E-signatures are often more affordable and easier to implement, making them ideal for small businesses and individuals.
Digital signatures may require more investment in technology and training but offer unparalleled security.
4. Geographical considerations
Some countries have specific requirements for electronic signatures. For example, the EU’s eIDAS Regulation distinguishes between standard e-signatures and qualified electronic signatures (QES), which are essentially digital signatures. (Erm, can’t they just be called digital signatures then?)
Seamlessly integrate e-signatures into your workflow
The sales process should be simple! Qwilr’s e-signature function offers a smooth, hassle-free way to close deals and agreements without the need for printing or scanning. Integrated directly into Qwilr’s smart proposals, it allows clients to sign documents electronically, ensuring the process is not only faster but also more secure.
Whether you’re in a rush or working with clients across the globe, Qwilr makes it simple to get those sales contracts signed with a few clicks, all while maintaining the professionalism and security you need. It’s a modern, seamless way to manage agreements - no fuss, just results.
Easy, efficient e-signatures with Qwilr
Digital signatures and e-signatures both play vital roles in today’s digital landscape, but they serve different purposes. Why settle for less security when the stakes are high? Can convenience outweigh the risks in sensitive transactions?
E-signatures prioritize convenience and accessibility, making them ideal for everyday business transactions. Digital signatures, on the other hand, provide unmatched security and compliance, making them the go-to choice for industries where trust and reliability are paramount. Hopefully, the differences are clear as day, now.
It feels good to keep up with the times. Sign up for a free trial and experience the endless benefits Qwilr has to offer.
About the author

Brendan Connaughton|Head of Growth Marketing
Brendan heads up growth marketing and demand generation at Qwilr, overseeing performance marketing, SEO, and lifecycle initiatives. Brendan has been instrumental in developing go-to-market functions for a number of high-growth startups and challenger brands.